Recent discussions about Gmail’s smart features have led to questions about how Google uses user data. The settings mention that turning these features on allows Google to use your information and activity to personalize the experience. This wording led Malwarebytes and blogger Dave Jones to assume that user content was being used to train AI models. Google has stated that this assumption is incorrect.
IMPORTANT message for everyone using Gmail.
— Dave Jones (@eevblog) November 19, 2025
You have been automatically OPTED IN to allow Gmail to access all your private messages & attachments to train AI models.
You have to manually turn off Smart Features in the Setting menu in TWO locations.
Retweet so every is aware. pic.twitter.com/54FKcr4jO2
Users who want to review or change these options can find them by clicking the gear icon in Gmail’s top-right corner. Under “Settings,” in the “General” tab, the smart features appear in two separate sections near the bottom of the page.
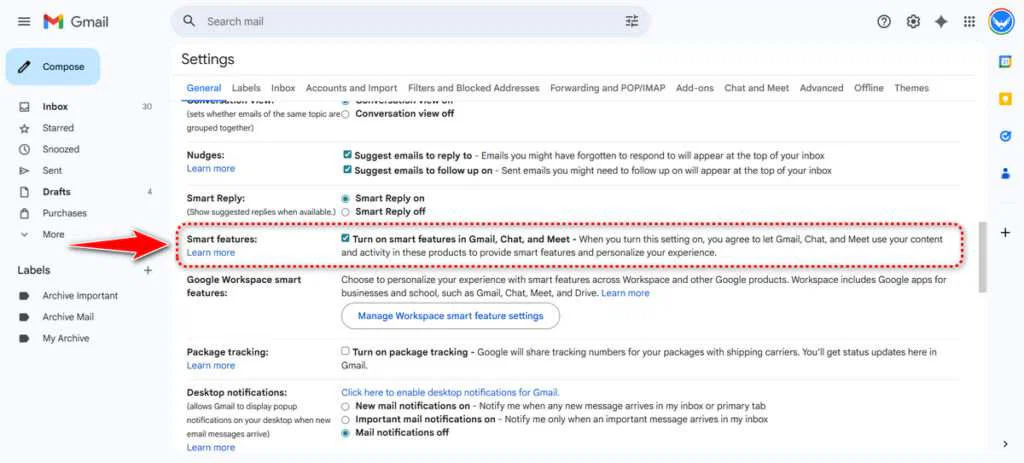
The first section covers smart features used across Gmail, Chat, and Meet, including tools like spell check, spam filtering, and automatic sorting. A separate button leads to the “Workspace smart features” menu, which has its own set of controls. These manage newer functions such as showing Gmail events in Google Calendar, producing AI-generated summaries, and handling restaurant reservations. Any updates require clicking “Save” and reloading the page.
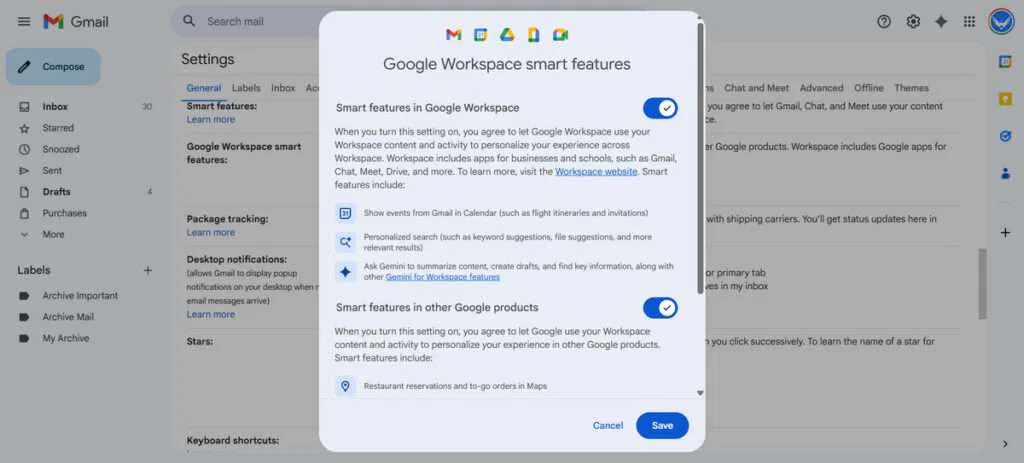
Google has responded to the concerns by clarifying that Gmail user content is not used to train its Gemini AI. It also reminded folks that tools like spam filters have been around for a long time. The “Workspace” menu may reference some new Gemini features, but Google says that’s not the same as feeding your private emails into its models. The company also insists it isn’t switching settings on its own, though a few users say they’ve had trouble turning certain features off.
Let's set the record straight on recent misleading reports. Here are the facts:
— Gmail (@gmail) November 21, 2025
• We have not changed anyone’s settings.
• Gmail Smart Features have existed for many years.
• We do not use your Gmail content to train our Gemini AI model.
We are always transparent and…
AI has been woven into Gmail step by step. Google began leveraging the technology in late 2023 to upgrade its spam blocker, followed in 2024 by the rollout of an AI-assisted writing tool. The latest updates include default AI-generated summaries on mobile and additional AI enhancements to Gmail’s search function.
Aside from privacy issues, the broader use of AI in email has revealed some security risks. According to a March report from Mozilla, attackers might be able to use prompt injections to alter Gmail’s AI summaries and redirect them toward phishing attempts.
What’s happening with Gmail is part of a bigger story. Facebook, LinkedIn, Slack, and YouTube have all dipped into user content to train their AI at different points. And now the hunt for training data is moving off the screen, as researchers watch and record the real world to teach tomorrow’s AI-driven robots how to move and react.
Maybe you would like other interesting articles?

